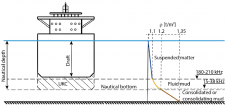
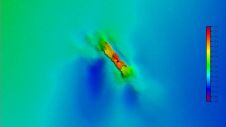
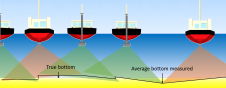
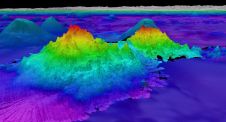
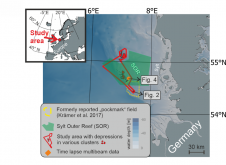
Mapping through fluid mud
The presence of suspended sediments in water bodies presents significant challenges for the dredging industry. Existing methods to determine nautical depths are intrusive single point methods relying on in situ density or shear strength measurements1,3 or low-frequency single-beam echosounder recordings1,2. The use of single-beam echosounders is however systemically problematic as they are not practical in satisfying the CATZOC A1 coverages required for contemporary electronic navigational charting. The presence of suspended sediments in water bodies presents significant challenges for the dredging industry. Existing methods to determine nautical depths are intrusive single point methods relying on in situ...